Do you still have questions? We will be happy to help you.
*1 https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kohlenstofffaser

Anyone who has ever dealt with modern heating solutions has certainly already come across carbon heating films. These are often referred to as infrared heating films or electric surface heating. But what exactly is behind this particularly efficient technology and what areas of application are there? And what does Thomas Alva Edison, the inventor of the light bulb, have to do with it? With us you will find out...
The term "carbon" used in common parlance has developed from the English language and actually stands for carbon fibres.
Carbon fibres are industrially manufactured fibres made from organic raw materials. Known carbon deposits are, for example, the fossil fuels coal, crude oil and natural gas. Through a pyrolysis process, in which the starting materials are treated with temperatures of up to 1500 °C, a change in the atomic structure takes place. This results in a gaseous separation of all elements except for the main component carbon, which reaches a ratio of 96 to 98 percent by weight.
The special properties of carbon fibres are that they are electrically and thermally very conductive. This was already known to Thomas Alva Edison, who received a patent as early as 1881 for the carbon fibre incandescent lamp he developed with filaments made of pyrolysed bamboo fibres. *1
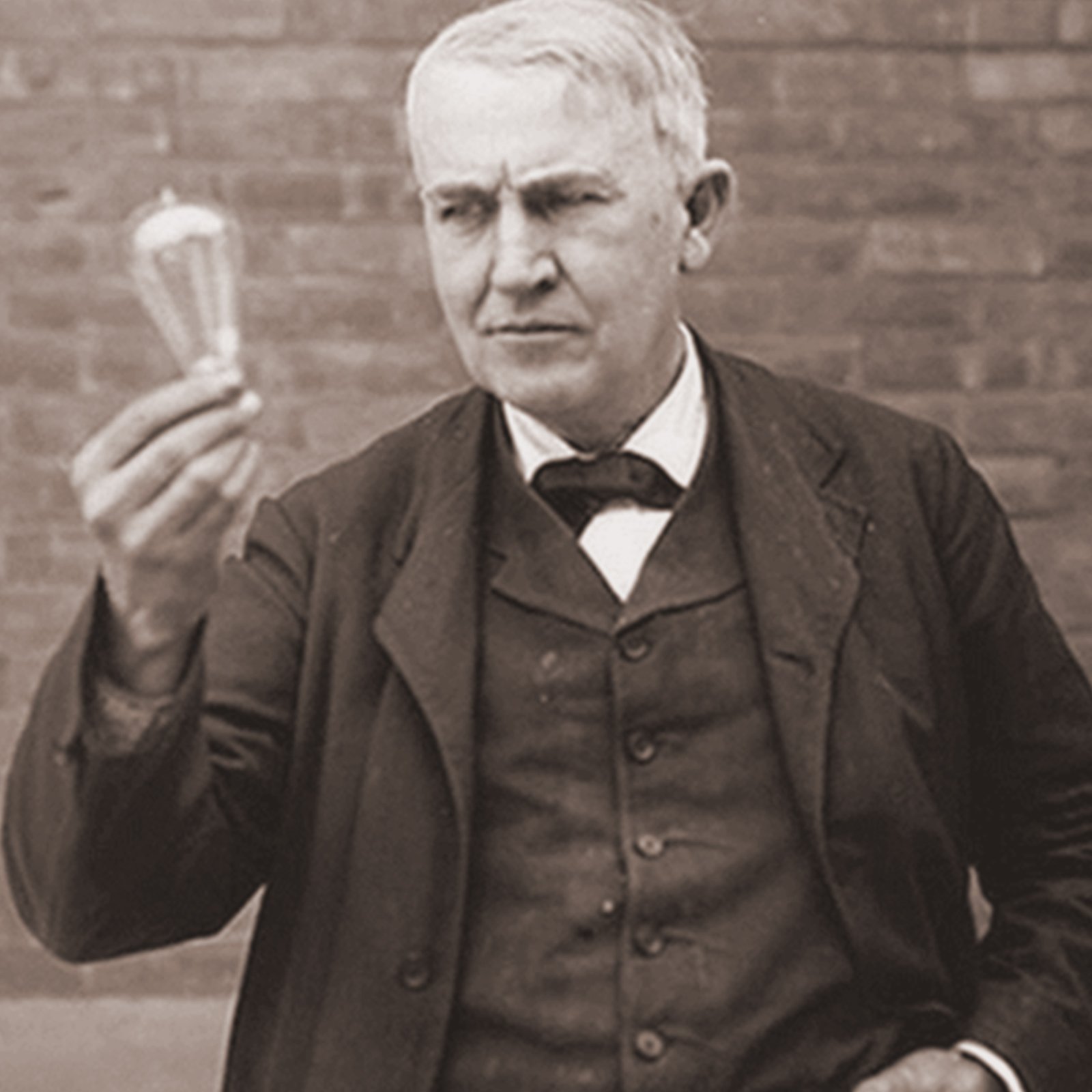

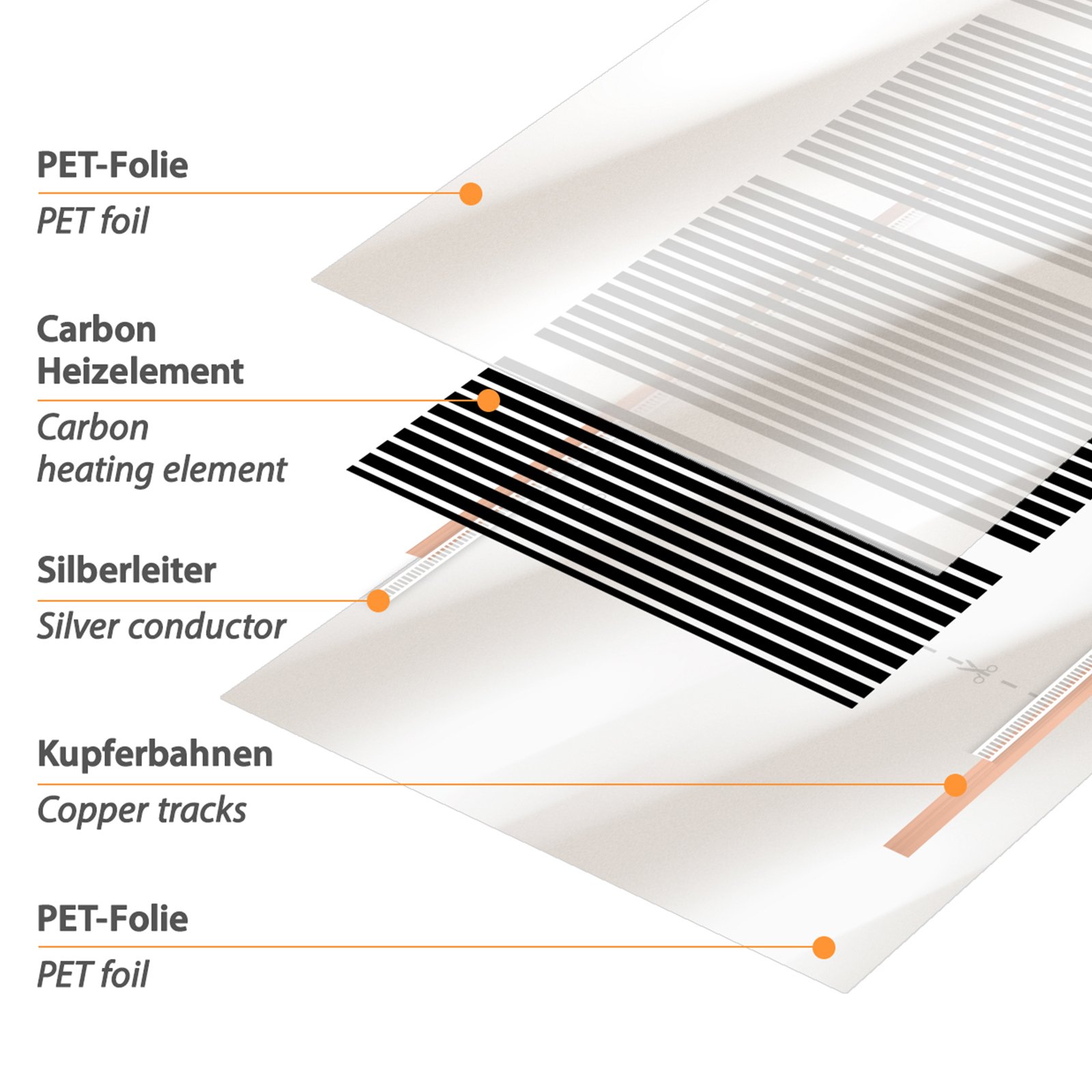
In tried and tested production processes, special carbon pastes are then made from the previously produced carbon fibres, which serve as the basis for standard heating films. However, the most modern production methods currently rely on shaping the extracted carbon into microscopically small carbon nanotubes. These carbon nanotubes, also known as carbon nanotubes (CNTs), are honeycomb-like lattices of carbon atoms and have diameters of 1 to 50 nanometres. This hitherto unique technology enables a significant gain in efficiency.
In further steps, the carbon pastes or carbon nanotubes are applied together with two copper strips to thin PET films. Additional silver strips are applied in the transverse direction, which ensure an optimal current flow onto the carbon material. Up to 6 additional layers of robust and waterproof PET film ensure the necessary durability and stability of the heating film.
The so-called fleece-laminated heating films have a similar structure. Here, however, a diffusion-open and adhesion-optimised fleece lamination is used instead of the smooth PET films. Thanks to the perforation, this heating film is optimally suited for plaster systems and levelling compounds on ceiling, wall and floor installations.
As soon as a voltage is applied to the copper bands of the heating films, the carbon material heats up and uniformly emits long-wave infrared radiation with an IR wavelength of 7-14 micrometres (IR-C radiation) similar to that of the sun.
Incidentally, the effect of the carbon heating films can also be compared with the sun. When the infrared rays hit solid bodies, they cause the molecules on the surface to vibrate. This creates warmth, which many people find particularly pleasant.
The installation heights of carbon heating films are usually between 0.366 mm and 0.60 mm, depending on the model, and are thus among the thinnest variants of electric heating systems.
In residential and commercial properties, carbon heating systems are usually used as surface heating systems. They emit the cosy radiant heat, e.g. via floors, walls or ceilings, to the respective room. Unlike conventional radiators (convectors), the air is only heated indirectly. As a result, convection of the heat and the associated circulation of the air are largely absent, so that less dust is stirred up. This is particularly pleasing for allergy sufferers.
In connection with electric panel heating, it is important to know that the perceived temperature in a room is made up of the air temperature and the surface temperature of the respective objects. So if the walls, floors and objects in a room are warm, we feel comfortable even at lower air temperatures. And lower air temperatures are in turn associated with lower heat losses, as well as lower heating costs. Studies have shown that the room temperature can be around two degrees Celsius lower when infrared heaters are used, without any loss of comfort. Just lowering the room temperature by only 1°C can result in energy savings of 5-7%.
In addition, a carbon heater converts electrical energy into heating energy with almost no losses, which is why this technology is considered particularly efficient. The effective heating power of heating films is always given as power per square metre and ranges from approx. 50 to 1500W/m². In residential and commercial spaces, however, the heating output ranges at a maximum of 200W/m²; carbon heating films above this threshold are more likely to be used for DIY projects or industrial purposes.
When heating properties, another advantage of electric panel heating, apart from the purely visual aspects, is the relative saving of space. This is because the heating films disappear quasi invisibly under floor coverings or wall or ceiling panelling and do not take up any of the usable space in the rooms.
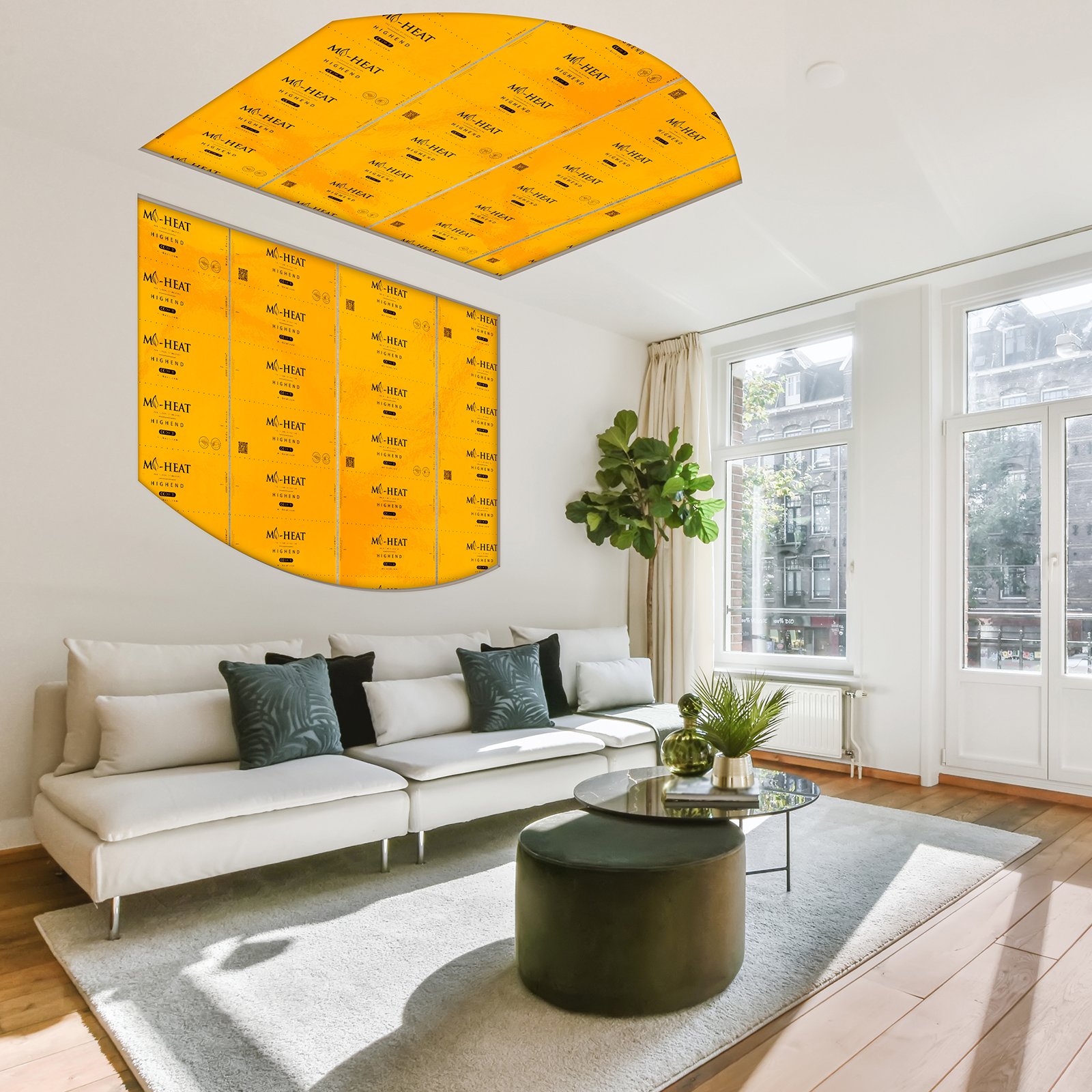
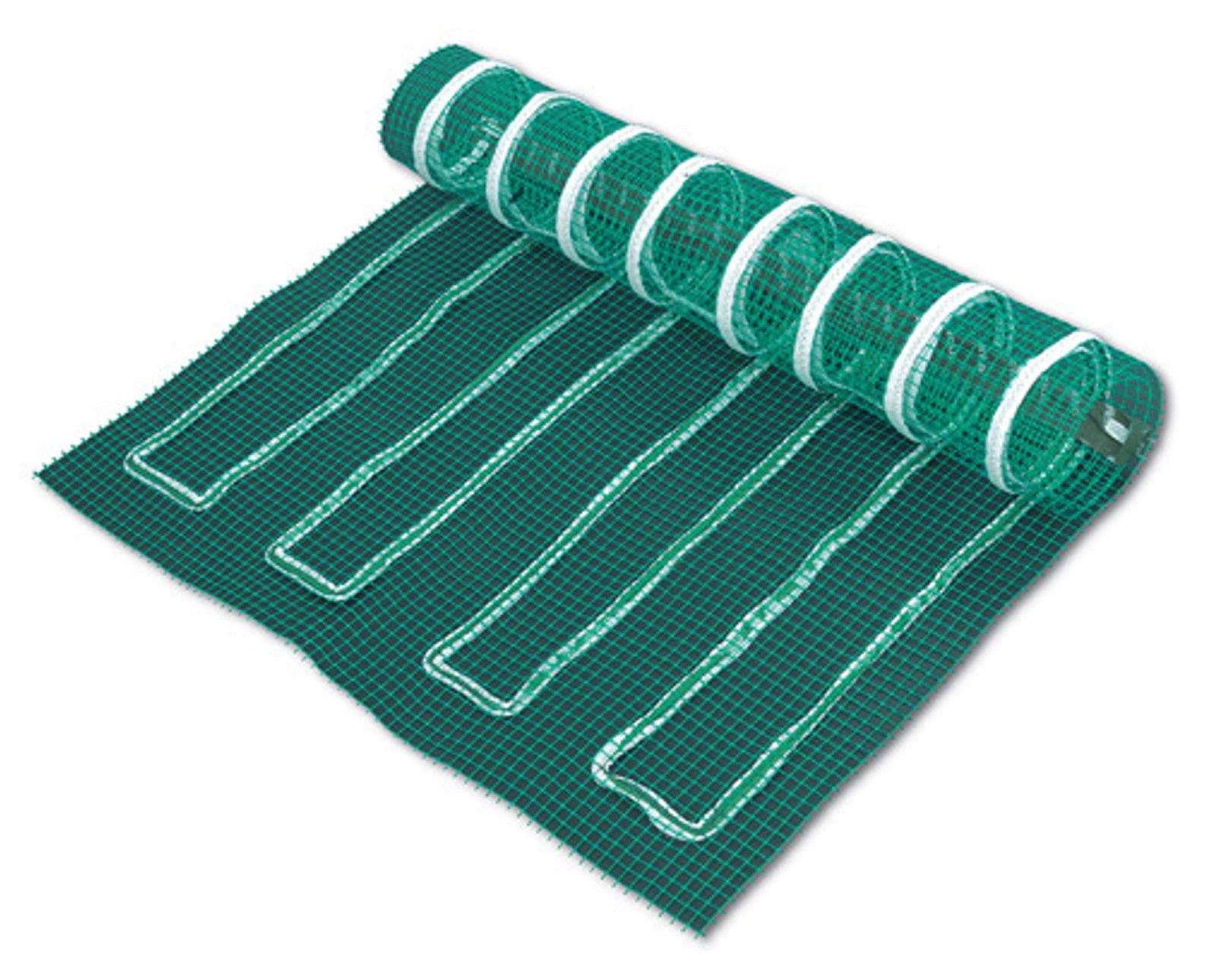


In addition to the use in heating films, carbon fibres are also used in infrared heating panels, textile heating elements, carbon heating paint or special carbon fibre underfloor heating mats.
The functional principle is the same in all applications. The current-carrying carbon material immediately generates long-wave infrared radiation, which provides a pleasant feeling of warmth after a very short lead time.
Especially in the area of thin-bed heating mats or heating cables, models with a carbon fibre heating conductor are clearly ahead of those with a conventional copper heating conductor. The heating of a carbon-fibre heating conductor is considerably faster, which results in lower power consumption for the same performance and climatic conditions. Thus, savings of up to 40% are possible.
In addition to room heating, our Mi-Heat carbon heating elements are also suitable for a variety of individual DIY projects for warming, heating or tempering. For example, Mi-Heat products are used in the following projects:

Do you still have questions? We will be happy to help you.
*1 https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Kohlenstofffaser